- home
-
news
- arXiv
- physics
- linux
- nature
- world
- BBC
- Al Jazeera
- earth
- universe
- wiki
- gemini
- NASA Earth Observatory (2025) El Niño. Accessed December 15, 2025.
- NASA Earth Observatory (2025, February 6) La Niña is Here. Accessed December 15, 2025.
- NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (2025) Ocean Surface Topography From Space. Accessed December 15, 2025.
- NOAA Climate Prediction Center (2025, December 11) El Niño/Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Diagnostic Discussion. Accessed December 15, 2025.
- World Meteorological Organization (2025, December 4) WMO Update predicts weak La Niña. Accessed December 15, 2025.
- 541715 – Research and Development in the Physical, Engineering, and Life Sciences (except Nanotechnology and Biotechnology)
- Biswal, A., et al. (2025) Emission time and amount of crop residue burning play critical role on PM2.5 variability during October–November in northwestern India during 2022–2024. Environmental Science: Atmospheres, 11.
- Burki, T. (2025) Stubble: The Farmer’s Bane. The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, 13(2), 207.
- The Deccan Herald (2025, December 8) Punjab, Haryana farmers change stubble burning time window to avoid satellite detection. Accessed December 9, 2025.
- Down to Earth (2025, November 26) Why has Madhya Pradesh burnt more paddy stubble for the second year in a row? Accessed December 9, 2025.
- Jethva, H., et al. (2019) Connecting Crop Productivity, Residue Fires, and Air Quality over Northern India. Scientific Reports, 9, 16594.
- Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (2025, December 1) Paddy Harvesting Season 2025 concludes with significant Reduction in Farm Fire Incidents across Punjab and Haryana. Accessed December 9, 2025.
- NASA (2024, October 18) What is Air Quality? Accessed December 9, 2025.
- NASA Earth Observatory (2020, November 17) A Busy Season for Crop Fires in Northwestern India. Accessed December 9, 2025.
- NASA Earth Observatory (2025, January 22) Is Fire Activity Declining in Northwestern India? Accessed December 9, 2025.
- NDTV (2025, December 1) Stubble Burning Down By 90% In Punjab, Haryana, Centre Informs Parliament. Accessed December 9, 2025.
- NDTV (2025, December 9) Farm Fires Didn’t End, They Just Moved To Afternoon: Satellite Data Analysis. Accessed December 9, 2025.
- The New Indian Express (2025, November 11) AQI spikes to 428 in first ‘severe’ air day of this year, GRAP-III invoked in capital. Accessed December 9, 2025.
- Singh, N., et al. (2025) Evidence of shift in stubble burning timing over northwest India from geostationary satellite observations. Current Science, 129(10), 921-923.
- The Times of India (2025, December 6) Stubble burning cases jump by 18% in UP this year. Accessed December 9, 2025.
A Subtle Return of La Niña
A weak La Niña emerged in the equatorial Pacific in late 2025, and scientists are watching how it may help shape weather and climate in the months ahead.https://science.nasa.gov/earth/earth-observatory/a-subtle-return-of-la-nina/
A Subtle Return of La Niña
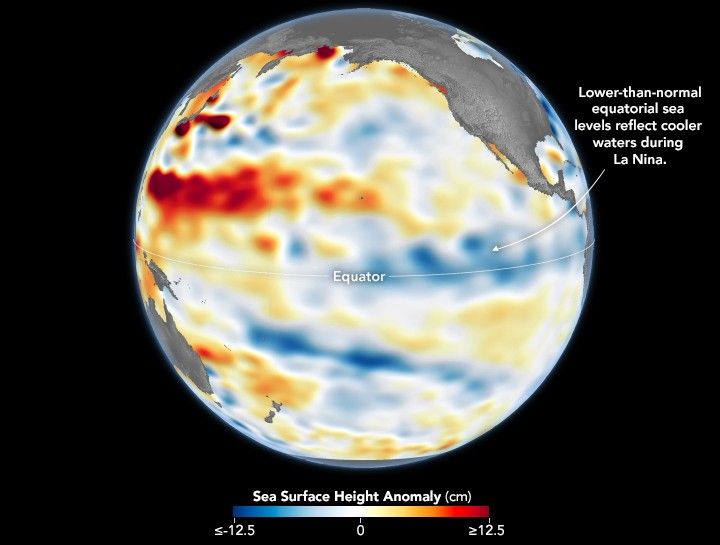
After a several-month hiatus, La Niña returned to the equatorial Pacific Ocean in September 2025 and has continued into December. However, this occurrence of El Niño’s cooler counterpart is relatively weak, and its influence on weather and climate over the next several months remains to be seen.
Part of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle, La Niña develops when strengthened easterly trade winds intensify the upwelling of cold, deep water in the eastern tropical Pacific. This process cools large swaths of the eastern and central equatorial Pacific while simultaneously pushing warm surface waters westward toward Asia and Australia. In a report published on December 11, the NOAA Climate Prediction Center confirmed that below-average sea surface temperatures associated with La Niña conditions were present and likely to continue for another month or two.
The shifting wind patterns and the movement of heat within the ocean have a direct impact on sea level. Because cooler water is denser and occupies less volume than warm water, sea levels in the central and eastern Pacific drop during La Niña events. The map above shows sea surface height observed on December 1, 2025. Shades of blue indicate below-normal sea levels, shades of red show above-normal levels, and white represents near-normal conditions.
Data for the map were acquired by the Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite and processed by scientists at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). Signals related to seasonal cycles and long-term trends have been removed to highlight sea level changes associated with ENSO and other short-term natural phenomena. The satellite’s twin successor, Sentinel-6B, launched in November 2025 and is expected to begin contributing to ENSO research and forecasts sometime in 2026.
This equatorial surface-water cooling alters the exchange of heat and moisture between the ocean and atmosphere, reshaping global atmospheric circulation patterns. La Niña’s coupling with the ocean and atmosphere can shift mid-latitude jet streams, intensifying rainfall in some regions while bringing drought to others.
Typically, La Niña years bring below-average rainfall to the American Southwest and above-average rainfall to the Northwest. But when the event is weak—whether El Niño or La Niña—the associated weather patterns can be “notoriously difficult to predict,” said Josh Willis, an oceanographer and Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich project scientist at JPL in Southern California.
“It still has the potential to tilt our winter toward the dry side in the American Southwest,” Willis said. “But it’s never a guarantee, especially with a mild event like this one.”
NASA Earth Observatory image by Lauren Dauphin, using modified Copernicus Sentinel data (2025) processed by the European Space Agency and further processed by Josh Willis and Kevin Marlis/NASA/JPL-Caltech. Story by Kathryn Hansen.
References & Resources
You may also be interested in:
Stay up-to-date with the latest content from NASA as we explore the universe and discover more about our home planet.

Sea ice around the southernmost continent hit one of its lowest seasonal highs since the start of the satellite record.

One of NASA’s newest Earth-observing sensors extends and improves the continuous measurement of light-harvesting pigments in ocean surface waters.

A multi-year drought has put extra strain on farmers and water managers in the Middle Eastern country.
Discover More from NASA Earth Science
https://science.nasa.gov/earth/earth-observatory/a-subtle-return-of-la-nina/
NextSTEP-3 B: Moon to Mars Architecture Studies
Notice ID: M2M-MSFC-0001 NAICS Codes: NASA seeks industry-led architecture concept development, concept refinement studies, and risk-reduction activities that address Moon to Mars Architecture gaps through the Next Space Technologies for Exploration Partnerships-3 (NextSTEP-3). NASA plans to release this solicitation — NextSTEP-3 Appendix B: Moon to Mars Architectural Studies — near the beginning of calendar year […]https://www.nasa.gov/general/nextstep-3-b-moon-to-mars-architecture-studies/
NextSTEP-3 B: Moon to Mars Architecture Studies
Notice ID: M2M-MSFC-0001
NAICS Codes:
NASA seeks industry-led architecture concept development, concept refinement studies, and risk-reduction activities that address Moon to Mars Architecture gaps through the Next Space Technologies for Exploration Partnerships-3 (NextSTEP-3). NASA plans to release this solicitation — NextSTEP-3 Appendix B: Moon to Mars Architectural Studies — near the beginning of calendar year 2026. For full details, consult the links under the notice ID above.
NASA’s Moon to Mars Architecture defines capabilities needed for long-term, human-led scientific discovery in deep space. The agency’s architecture approach distills agency-developed objectives into capabilities and elements that support exploration and science goals. NASA continuously evolves that blueprint for crewed exploration, setting humanity on a path to the Moon, Mars, and beyond by collaborating with experts across industry, academia, and the international community.
This proposed solicitation seeks partner participation on a recurring basis, targeting several calls per year for proposal submissions. The proposals should focus on topics addressing infrastructure, transportation, habitation, concepts of operations, and planetary science capabilities identified in the latest revision of the Architecture Definition Document. The solicitation establishes a flexible acquisition strategy that accommodates both directed-topic calls on specific areas of government interest, as well as open topic calls.
NASA anticipates the first Appendix B directed-topic study calls will focus on lunar and Mars mission concepts. NASA intends to issue a directed call for research into an integrated surface power infrastructure (or power grid) that can evolve to support increasingly ambitious lunar missions. (Note: this call excludes proposals addressing the Fission Surface Power System Announcement for Partnership Proposal but may include all technology solutions including alternate fission, solar hybrid, or other power grid approaches.)
Concurrently, NASA will issue a directed call for Mars crew transportation concept development, trade studies, and identification of risk reduction activities. This call would include in-space transportation, Mars surface access, and Mars ascent options for crew and cargo.
https://www.nasa.gov/general/nextstep-3-b-moon-to-mars-architecture-studies/
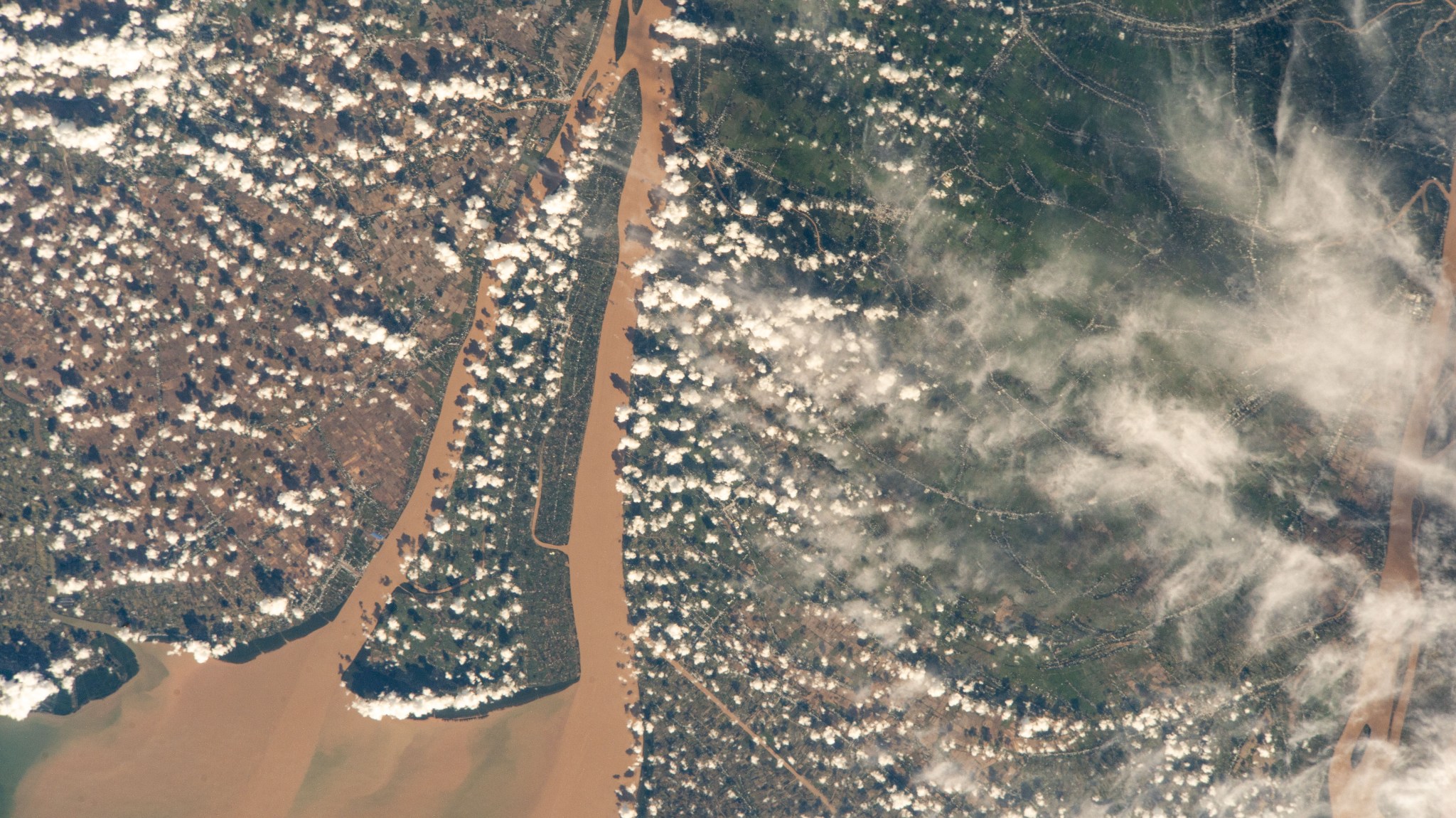
Bassac River, Southern Vietnam
A camera on the International Space Station captured this Oct. 2, 2025, photo of the Bassac River in Cù Lao Dung, a river islet district in southern Vietnam. The Bassac River surrounds the district before emptying into the South China Sea. The river’s brown waters at its mouth result from massive amounts of silt, clay, […]https://www.nasa.gov/image-article/bassac-river-southern-vietnam/
Bassac River, Southern Vietnam
A camera on the International Space Station captured this Oct. 2, 2025, photo of the Bassac River in Cù Lao Dung, a river islet district in southern Vietnam. The Bassac River surrounds the district before emptying into the South China Sea. The river’s brown waters at its mouth result from massive amounts of silt, clay, and organic matter carried from upstream regions of the Mekong River Basin, combined with tidal forces from the sea that stir up sediment. This photograph was taken from as the space station orbited 260 miles above Earth.
Image credit: NASA
https://www.nasa.gov/image-article/bassac-river-southern-vietnam/
NASA’s Roman Telescope Will Observe Thousands of Newfound Cosmic Voids
Lee esta nota de prensa en español aquí. Our universe is filled with galaxies, in all directions as far as our instruments can see. Some researchers estimate that there are as many as two trillion galaxies in the observable universe. At first glance, these galaxies might appear to be randomly scattered across space, but they’re not. […]https://www.nasa.gov/missions/roman-space-telescope/nasas-roman-telescope-will-observe-thousands-of-newfound-cosmic-voids/
NASA’s Roman Telescope Will Observe Thousands of Newfound Cosmic Voids
Lee esta nota de prensa en español aquí.
Our universe is filled with galaxies, in all directions as far as our instruments can see. Some researchers estimate that there are as many as two trillion galaxies in the observable universe. At first glance, these galaxies might appear to be randomly scattered across space, but they’re not. Careful mapping has shown that they are distributed across the surfaces of giant cosmic “bubbles” up to several hundred million light-years across. Inside these bubbles, few galaxies are found, so those regions are called cosmic voids. NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will allow us to measure these voids with new precision, which can tell us about the history of the universe’s expansion.
“Roman’s ability to observe wide areas of the sky to great depths, spotting an abundance of faint and distant galaxies, will revolutionize the study of cosmic voids,” said Giovanni Verza of the Flatiron Institute and New York University, lead author on a paper published in The Astrophysical Journal.
Cosmic Recipe
The cosmos is made of three key components: normal matter, dark matter, and dark energy. The gravity of normal and dark matter tries to slow the expansion of the universe, while dark energy opposes gravity to speed up the universe’s expansion. The nature of both dark matter and dark energy are currently unknown. Scientists are trying to understand them by studying their effects on things we can observe, such as the distribution of galaxies across space.
“Since they’re relatively empty of matter, voids are regions of space that are dominated by dark energy. By studying voids, we should be able to put powerful constraints on the nature of dark energy,” said co-author Alice Pisani of CNRS (the French National Centre for Scientific Research) in France and Princeton University in New Jersey.
To determine how Roman might study voids, the researchers considered one potential design of the Roman High-Latitude Wide-Area Survey, one of three core community surveys that Roman will conduct. The High-Latitude Wide-Area Survey will look away from the plane of our galaxy (hence the term high latitude in galactic coordinates). The team found that this survey should be able to detect and measure tens of thousands of cosmic voids, some as small as just 20 million light-years across. Such large numbers of voids will allow scientists to use statistical methods to determine how their observed shapes are influenced by the key components of the universe.
To determine the actual, 3D shapes of the voids, astronomers will use two types of data from Roman — the positions of galaxies in the sky and their cosmological redshift, the latter of which is determined using spectroscopic data. To convert redshift to a physical distance, astronomers make assumptions about the components of the universe, including the strength of dark energy and how it might have evolved over time.
Pisani compared it to trying to infer a cake recipe (i.e., the universe’s makeup) from the final dessert served to you. “You try to put in the right ingredients — the right amount of matter, the right amount of dark energy — and then you check whether your cake looks as it should. If it doesn’t, that means you put in the wrong ingredients.”
In this case, the appearance of the “cake” is the shape found by statistically stacking all of the voids detected by Roman on top of each other. On average, voids are expected to have a spherical shape because there is no “preferred” location or direction in the universe (i.e., the universe is both homogeneous and isotropic on large scales). This means that, if the stacking is done correctly, the resulting shape will be perfectly round (or spherically symmetric). If not, then you have to adjust your cosmic recipe.
Power of Roman
The researchers emphasized that to study cosmic voids in large numbers, an observatory must be able to probe a large volume of the universe, because the voids themselves can be tens or hundreds of millions of light-years across. The spectroscopic data necessary to study voids will come from a portion of the Roman High-Latitude Wide-Area Survey that will cover on the order of 2,400 square degrees of the sky, or 12,000 full moons. It will also be able to see fainter and more distant objects, yielding a greater density of galaxies than complementary missions like ESA’s (European Space Agency’s) Euclid.
“Voids are defined by the fact that they contain so few galaxies. So to detect voids, you have to be able to observe galaxies that are quite sparse and faint. With Roman, we can better look at the galaxies that populate voids, which ultimately will give us greater understanding of the cosmological parameters like dark energy that are sculpting voids,” said co-author Giulia Degni of Roma Tre University and INFN (the National Institute of Nuclear Physics) in Rome.
The Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope is managed at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, with participation by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California; Caltech/IPAC in Pasadena, California; the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore; and a science team comprising scientists from various research institutions. The primary industrial partners are BAE Systems, Inc. in Boulder, Colorado; L3Harris Technologies in Melbourne, Florida; and Teledyne Scientific & Imaging in Thousand Oaks, California.
By Christine Pulliam
Space Telescope Science Institute, Baltimore, Md.
cpulliam@stsci.edu
Explore More
Details
https://www.nasa.gov/missions/roman-space-telescope/nasas-roman-telescope-will-observe-thousands-of-newfound-cosmic-voids/
Unexpected Trajectory: Erin Sholl’s Path to Human Spaceflight Safety
Career paths are rarely a straight line and often include some unexpected curves. That is certainly true for Erin Sholl, deputy chief of the Space Transportation Systems Division within the Safety and Mission Assurance Directorate at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. From struggling with multiplication tables in elementary school to supporting the International Space […]https://www.nasa.gov/centers-and-facilities/johnson/unexpected-trajectory-erin-sholls-path-to-human-spaceflight-safety/
Unexpected Trajectory: Erin Sholl’s Path to Human Spaceflight Safety
Career paths are rarely a straight line and often include some unexpected curves. That is certainly true for Erin Sholl, deputy chief of the Space Transportation Systems Division within the Safety and Mission Assurance Directorate at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. From struggling with multiplication tables in elementary school to supporting the International Space Station from the Mission Control Center, her journey has been full of twists and turns.

Despite her early difficulties in math and science, Sholl eventually grew to love and excel in both subjects. She planned to study chemical engineering in college – inspired by a love of chemistry and a favorite high school teacher – but discovered a greater affinity for physics once she arrived at Pennsylvania State University. She switched her major to aerospace engineering and soon met a classmate who had interned at Johnson. After that, Sholl declared, “The dream was born!”
Her first position at Johnson was as a trajectory operations officer for the Flight Operations Directorate. She spent six years supporting the space station on console in the Mission Control Center, describing the experience as “something out of the movies.” When Sholl went looking for a new challenge, she landed in the Safety and Mission Assurance Directorate.
“I was drawn to the Operations and Visiting Vehicles Branch because it had many similar aspects to my previous position – real-time operations and visiting vehicles,” she said. “I worked various roles over the next 12 years, gradually taking on more responsibility, and eventually becoming a group lead, then branch chief.” Sholl also served as acting deputy chief for the Space Habitation Systems Division, which oversees the Operations and Visiting Vehicles Branch. Her performance drew the attention of the Space Transportation Systems Division’s chief. “He asked me to come be his deputy, and that is where I still am today!”
The Space Transportation Systems Division provides system safety, reliability, and risk analysis for human spaceflight programs. The division works with the different program offices to reduce risk through technical assessments and guidance on Safety and Mission Assurance requirements throughout program and project lifecycles.
Sholl works closely with the division chief to support strategic planning, budgeting, and operations. “A key part of my role is connecting with people – both inside and outside the division – to ensure smooth communication and representation of the team’s needs,” she said. She leverages her relationship-building and strategic thinking skills to lead initiatives that advance the division’s and the directorate’s goals and to mentor employees.

Sholl believes strongly in the power of mentorship. “Having various mentors, both formal and informal, has been so important throughout my career,” she said. “Listening to what these people were saying about my strengths led me to a path I’d never considered because I hadn’t seen those things in myself.” Being a mentor and advocate for team members is one of Sholl’s favorite parts of the leadership positions she has held, particularly as branch chief. “I really felt like I could connect with my people and advocate for them in a way that felt meaningful,” she said.
She encourages young professionals to seek out mentors or opportunities to shadow colleagues in different roles. “Relationships are the key to everything,” she said. “The more people you meet and the more you learn about different paths in space exploration, the better off you will be in your career.”
Sholl noted that professional relationships can be bolstered by activities outside of the office. She played a key role in establishing and growing JSC Parenting, a virtual community of about 600 employees who share information and support each other on issues related to caregiving, schooling, and balancing work with family life. “My leadership within the community enhances my professional leadership and positively impacts my colleagues,” she said.
Sholl also emphasized the importance of being open to trying new things, even if an opportunity seems to diverge from your expected career path. “I volunteer for everything because I am always eager to learn more and find out what else I might be good at and how else I can serve my team,” she said. “I think it’s easy to feel intimidated hearing about other people’s career paths, because they often sound so perfectly planned and successful. You rarely hear about the pivots, setbacks, or decisions made for personal reasons.”
The reality, she added, is more complex. “I tried for many roles I didn’t get, and it took a lot of trial and error to find my path to a career I really love.”
Explore More
https://www.nasa.gov/centers-and-facilities/johnson/unexpected-trajectory-erin-sholls-path-to-human-spaceflight-safety/
New Timing for Stubble Burning in India
Scientists say the seasonal crop fires are burning later in the day than in previous years.https://science.nasa.gov/earth/earth-observatory/new-timing-for-stubble-burning-in-india/
New Timing for Stubble Burning in India
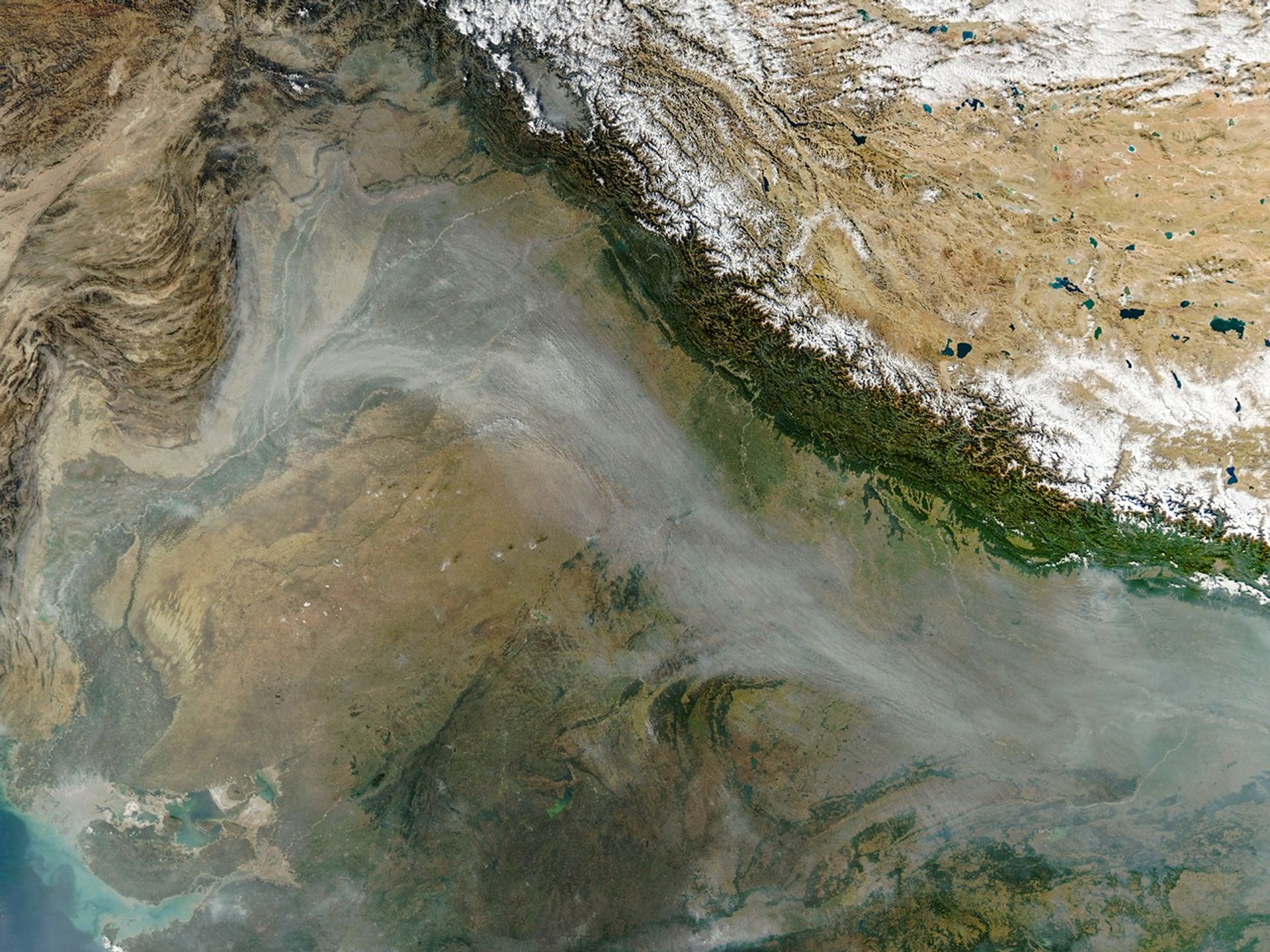
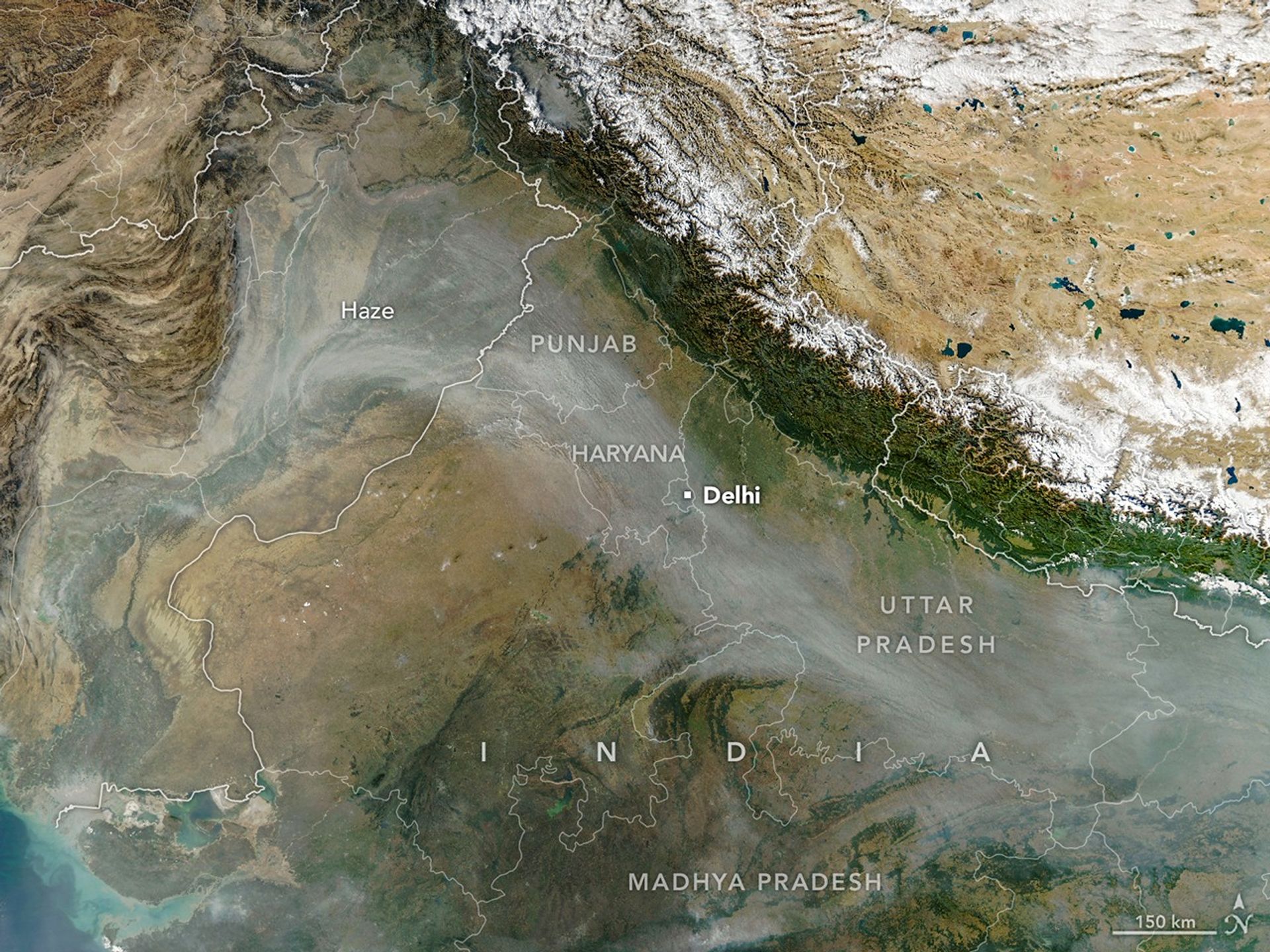
Every year for decades, long rivers of smoke and haze have spread across the Indo-Gangetic Plain in northern India from October to December. That’s when farmers in Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, and other states burn off plant “stubble” after the rice harvest.
When winds are weak and the atmosphere becomes stagnant, the haze can push levels of air pollution several times higher than limits recommended by the World Health Organization. Smoke typically mixes with particles and gases from other sources, such as industry, vehicles, domestic fires (heating and cooking), fireworks, and dust storms, to form the haze, though scientists consider stubble burning to be a major factor.
In some ways, the seasonal timing of stubble fires in 2025 followed typical patterns. Air quality deteriorated in Delhi and several other cities for about a month after crop fires intensified during the last week of October, explained Hiren Jethva, a Morgan State University atmospheric scientist based at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center. For about a decade, Jethva has tracked the stubble burning season in India using satellites, and has made predictions about the intensity of the upcoming fire season based on vegetation observations.
The MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) on NASA’s Aqua satellite captured this image of a smoky haze darkening skies over much of the plain on November 11, 2025. According to news reports, it was the first of several days in 2025 when pollution levels exceeded 400 on India’s air quality index, the strongest rating on the scale. As in past years, the poor air quality prompted officials in some areas to close schools and institute more stringent air quality controls on construction.
However, the daily timing of burning departs from what Jethva has seen in the past. He started tracking the number of fires years ago by primarily tallying observations from MODIS—which pass over locations on Earth each morning and afternoon on the Terra and Aqua satellites, respectively. Then, most fires were lit in the early afternoon between 1 p.m. and 2 p.m. local time.
But in the past few years, stubble fires have occurred progressively later in the day, Jethva said. He identified the shift by analyzing observations from GEO-KOMPSAT-2A, a South Korean geostationary satellite launched in late 2018 that collects data every 10 minutes.
Most stubble fires now happen between 4 p.m. and 6 p.m., he said, meaning that fire-monitoring systems that rely solely on MODIS, or similar sensors like VIIRS (Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite), miss many of the fires. “Farmers have changed their behavior,” he said.
His analysis of GEO-KOMPSAT-2A observations indicates that the stubble burning activity in Punjab and Haryana was moderate in 2025 compared to other recent years. This year had higher numbers of fires compared to 2024, 2020, and 2019 but fewer fires than 2023, 2022, and 2021, he found.
Indian Space Research Organization researchers have also pointed out the shift in the timing of stubble burning. In a Current Science study published in 2025, one group reported that MSG (Meteosat Second Generation) satellite observations showed a shift in peak fire activity from about 1:30 p.m. in 2020 to about 5:00 p.m. in 2024. In December 2025, researchers with the International Forum for Environment, Sustainability, & Technology (iForest) released a multi-satellite analysis that came to a similar conclusion.
Meanwhile, parsing out precisely how much stubble fires contribute to poor air quality in Delhi compared to other sources of pollution remains a topic of active study and debate among scientists. “Studies report contributions ranging from 10 to 50 percent,” said Pawan Gupta, a NASA research scientist who specializes in air quality.
Gupta estimates that the stubble burning contribution ranges from 40 to 70 percent on a given day, dropping to 20 to 30 percent if averaged over a month or burning season, and under 10 percent if averaged annually. “Meteorological conditions—like a shallow boundary layer height and low temperature—during the burning season add extra complexity,” he said.
The timing of the fires may influence the degree to which stubble burning affects air quality. Some modeling research suggests that evening fires may lead to a stronger overnight buildup of particle pollution than early-afternoon fires because the planetary boundary layer, the lowest part of the atmosphere, tends to be shallower and have weaker winds at night, allowing pollutants to accumulate.
NASA Earth Observatory image by Michala Garrison, using MODIS data from NASA EOSDIS LANCE and GIBS/Worldview. Story by Adam Voiland.
References and Resources
You may also be interested in:
Stay up-to-date with the latest content from NASA as we explore the universe and discover more about our home planet.

Fires burning in boreal forests created hazy skies across North America in summer 2025.

As wildland fires raged in the American West, NASA airborne technology was there to image it in incredible detail.

Lightning likely ignited several large fires that sent smoke pouring over the Canadian province in early September 2025.
Discover More from NASA Earth Science
https://science.nasa.gov/earth/earth-observatory/new-timing-for-stubble-burning-in-india/
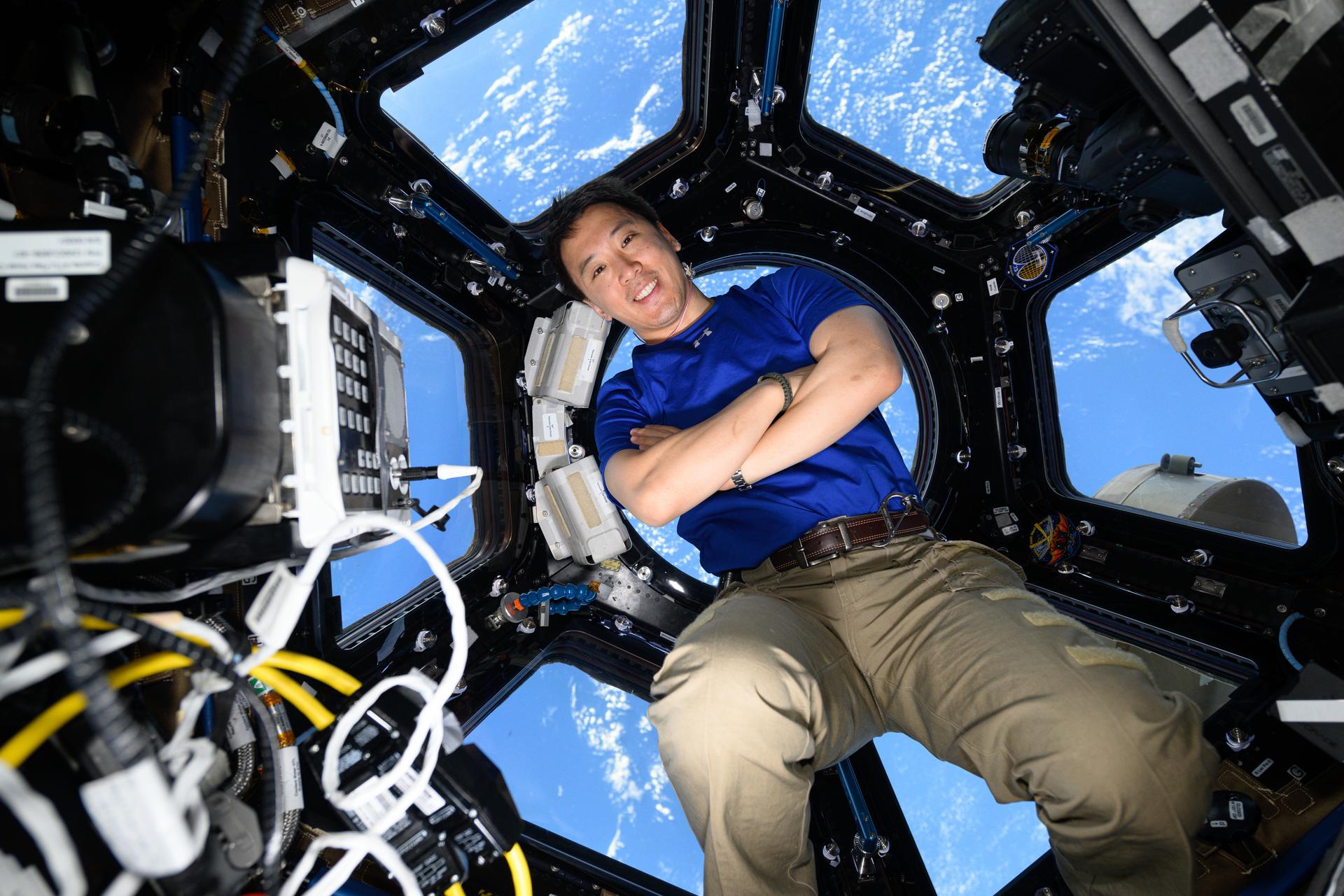
NASA Astronaut Jonny Kim to Discuss Eight-Month Space Station Mission
NASA astronaut Jonny Kim will recap his recent mission aboard the International Space Station during a news conference at 3:30 p.m. EST Friday, Dec. 19, from the agency’s Johnson Space Center in Houston. Watch the news conference live on NASA’s YouTube channel. Learn how to stream NASA content through a variety of online platforms, including […]https://www.nasa.gov/news-release/nasa-astronaut-jonny-kim-to-discuss-eight-month-space-station-mission/
NASA Astronaut Jonny Kim to Discuss Eight-Month Space Station Mission
NASA astronaut Jonny Kim will recap his recent mission aboard the International Space Station during a news conference at 3:30 p.m. EST Friday, Dec. 19, from the agency’s Johnson Space Center in Houston.
Watch the news conference live on NASA’s YouTube channel. Learn how to stream NASA content through a variety of online platforms, including social media.
Media interested in participating in person must contact the NASA Johnson newsroom no later than 5 p.m. Thursday, Dec. 18, at 281-483-5111 or jsccommu@mail.nasa.gov.
Media wishing to participate by phone must contact the Johnson newsroom no later than two hours before the start of the event. To ask questions by phone, media must dial into the news conference no later than 15 minutes prior to the start of the call. NASA’s media accreditation policy is available online.
Kim returned to Earth on Dec. 9, along with Roscosmos cosmonauts Sergey Ryzhikov and Alexey Zubritsky. He logged 245 days as an Expedition 72/73 flight engineer during his first spaceflight. The trio completed 3,920 orbits of the Earth over the course of their nearly 104-million-mile journey. They also saw the arrival of nine visiting spacecraft and the departure of six.
During his mission, Kim contributed to a wide range of scientific investigations and technology demonstrations. He studied the behavior of bioprinted tissues containing blood vessels in microgravity for an experiment helping advance space-based tissue production to treat patients on Earth. He also evaluated the remote command of multiple robots in space for the Surface Avatar study, which could support the development of robotic assistants for future exploration missions. Additionally, Kim worked on developing in-space manufacturing of DNA-mimicking nanomaterials, which could improve drug delivery technologies and support emerging therapeutics and regenerative medicine.
Learn more about International Space Station research and operations at:
-end-
Jimi Russell
Headquarters, Washington
202-358-1100
james.j.russell@nasa.gov
Shaneequa Vereen
Johnson Space Center, Houston
281-483-5111
shaneequa.y.vereen@nasa.gov
https://www.nasa.gov/news-release/nasa-astronaut-jonny-kim-to-discuss-eight-month-space-station-mission/
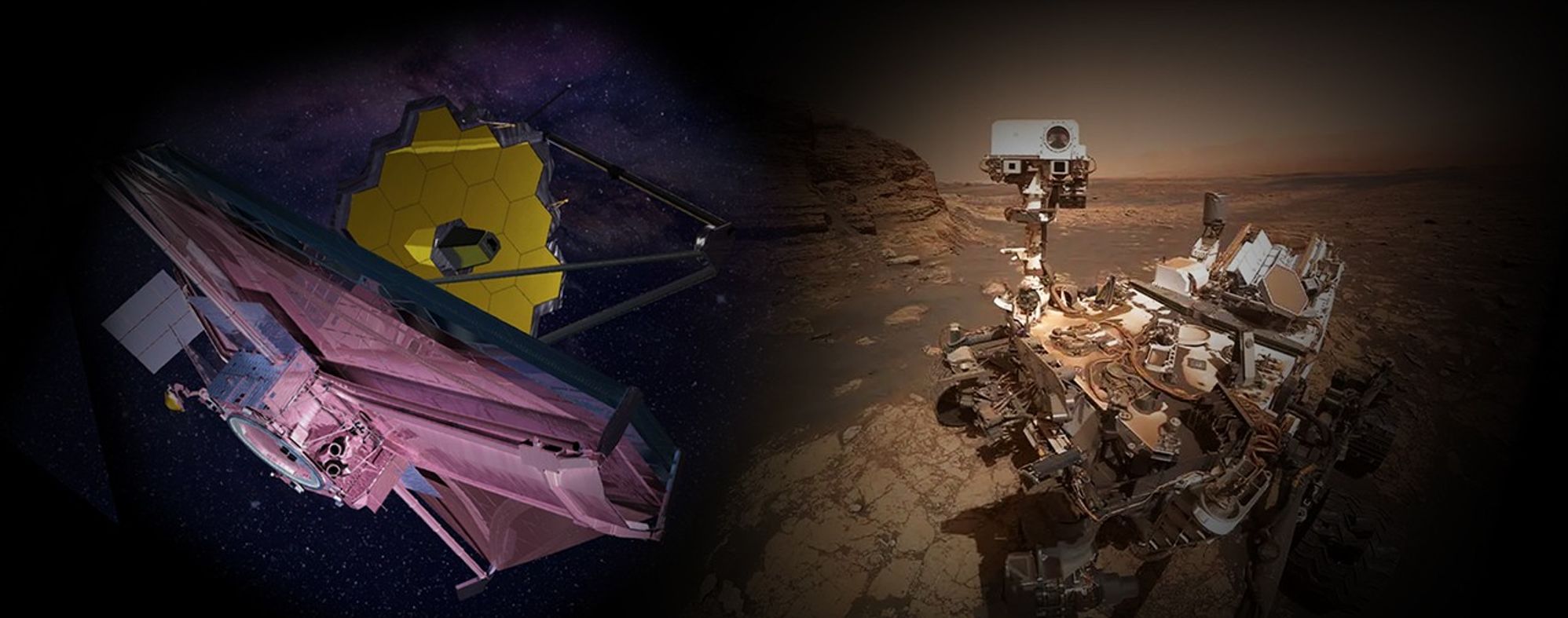
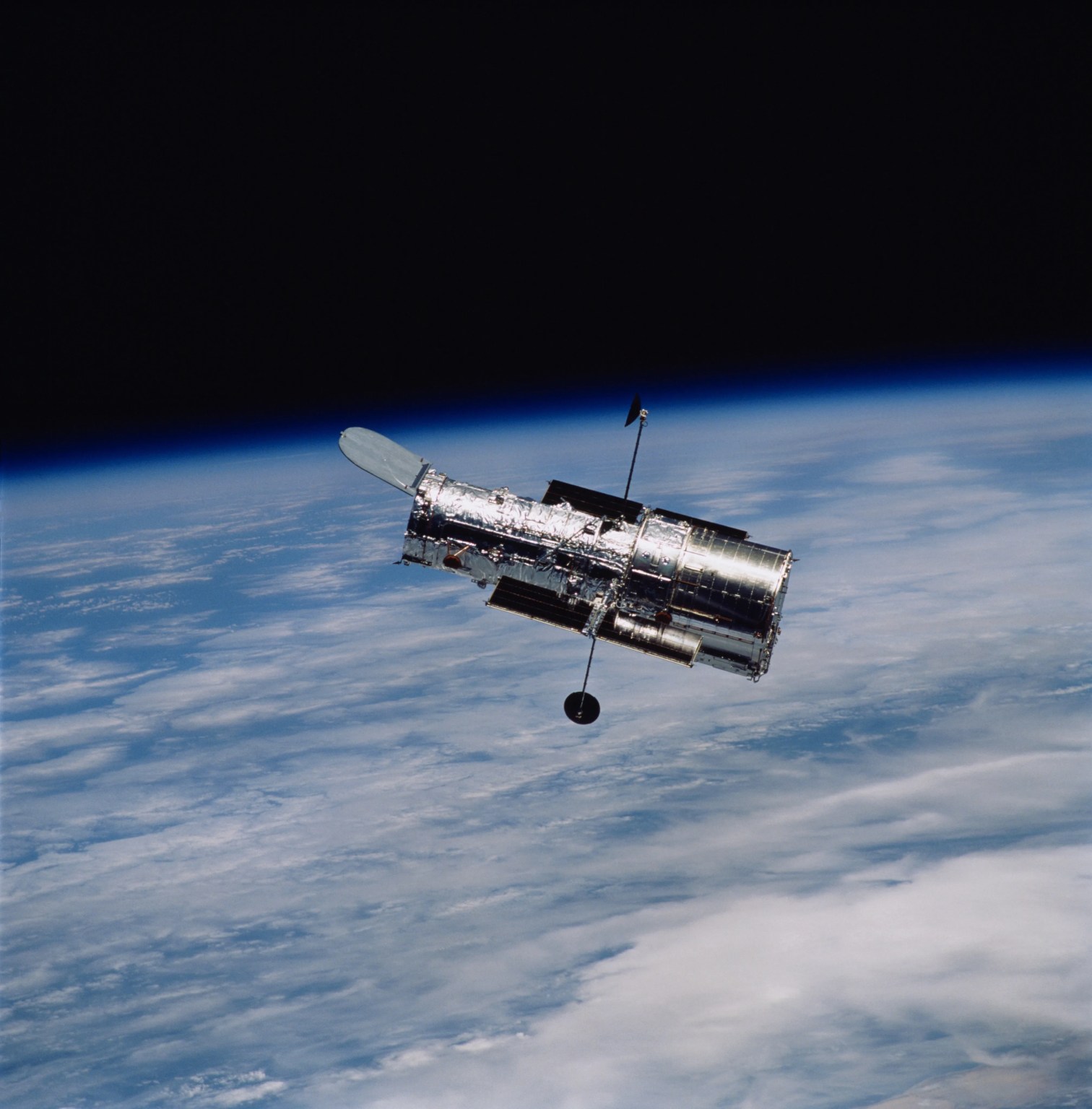
NASA’s Webb, Curiosity Named in TIME’s Best Inventions Hall of Fame
Two icons of discovery, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope and NASA’s Curiosity rover, have earned places in TIME’s “Best Inventions Hall of Fame,” which recognizes the 25 groundbreaking inventions of the past quarter century that have had the most global impact, since TIME began its annual Best Inventions list in 2000. The inventions are celebrated […]https://science.nasa.gov/missions/webb/nasas-webb-curiosity-named-in-times-best-inventions-hall-of-fame/
NASA’s Webb, Curiosity Named in TIME’s Best Inventions Hall of Fame
Two icons of discovery, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope and NASA’s Curiosity rover, have earned places in TIME’s “Best Inventions Hall of Fame,” which recognizes the 25 groundbreaking inventions of the past quarter century that have had the most global impact, since TIME began its annual Best Inventions list in 2000. The inventions are celebrated in TIME’s December print issue.
“NASA does the impossible every day, and it starts with the visionary science that propels humanity farther than ever before,” said Nicky Fox, associate administrator, Science Mission Directorate, NASA Headquarters in Washington. “Congratulations to the teams who made the world’s great engineering feats, the James Webb Space Telescope and the Mars Curiosity Rover, a reality. Through their work, distant galaxies feel closer, and the red sands of Mars are more familiar, as they expanded and redefined the bounds of human achievement in the cosmos for the benefit of all.”
Decades in the making and operating a million miles from Earth, Webb is the most powerful space telescope ever built, giving humanity breathtaking views of newborn stars, distant galaxies, and even planets orbiting other stars. The new technologies developed to enable Webb’s science goals – from optics to detectors to thermal control systems – now also touch Americans’ everyday lives, improving manufacturing for everything from high-end cameras and contact lenses to advanced semiconductors and inspections of aircraft engine components.

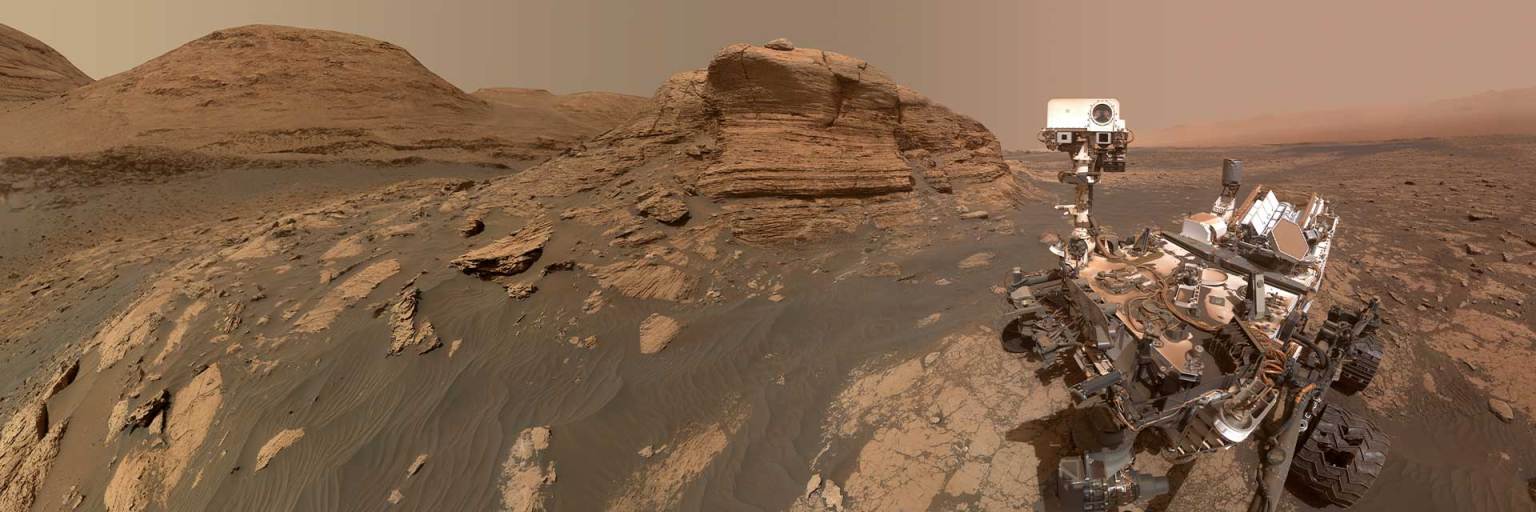
Meanwhile on Mars, the unstoppable Curiosity rover, NASA’s car-size science lab, has spent more than a decade uncovering clues that the Red Planet once could have supported life, transforming our understanding of our planetary neighbor. These NASA missions continue to make breakthroughs that have reshaped our understanding of the universe and our place in it. Curiosity has also paved the way for future astronauts: Its Radiation Assessment Detector has studied the Martian radiation environment for nearly 14 years, and its unforgettable landing by robotic jetpack allowed heavier spacecraft to touch down on the surface — a capability that will be needed to send cargo and humans to Mars.
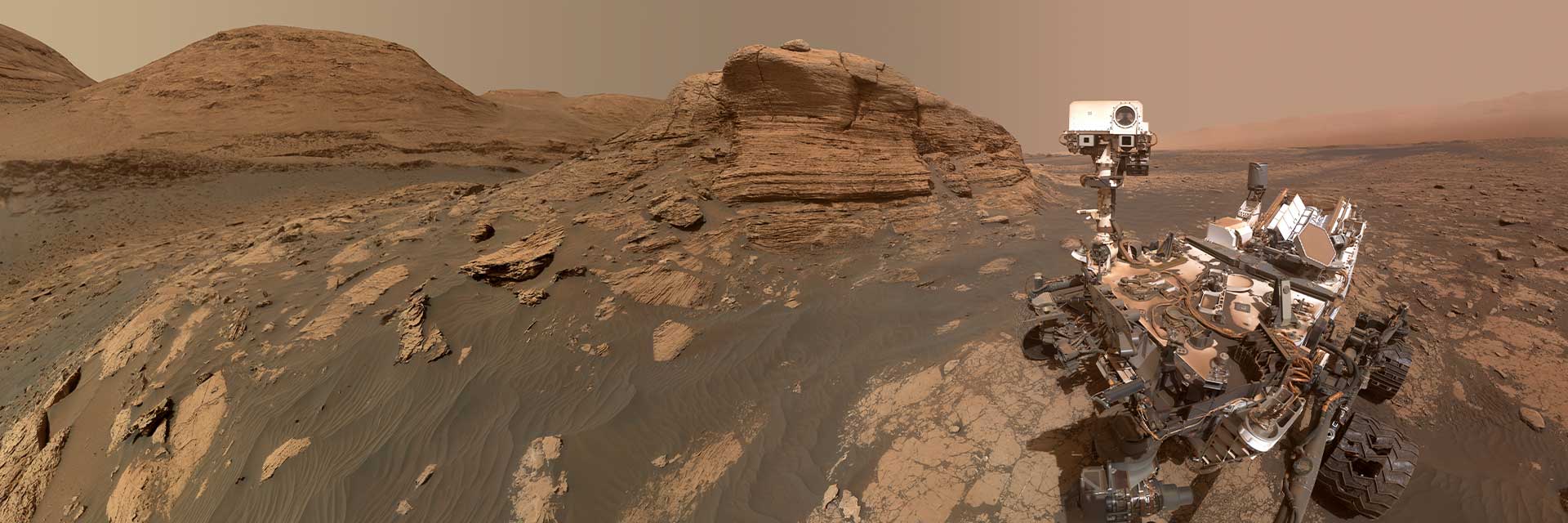

To compile this “Hall of Fame” list, TIME solicited nominations from TIME editors and correspondents around the world, paying special attention to high-impact fields, such as health care and technology. TIME then evaluated each contender on a number of key factors, including originality, continued efficacy, ambition, and impact.
The James Webb Space Telescope is the world’s premier space science observatory. Webb is solving mysteries in our solar system, looking beyond to distant worlds around other stars, and probing the mysterious structures and origins of our universe and our place in it. Webb is an international program led by NASA with its partners, ESA (European Space Agency) and CSA (Canadian Space Agency).
The Curiosity rover was built by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed by Caltech in Pasadena, California. JPL leads the mission on behalf of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington as part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program portfolio.
To learn more about NASA’s science missions, visit:
Discover More Topics From NASA
Explore NASA Science Activities

James Webb Space Telescope
Webb is the premier observatory of the next decade, serving thousands of astronomers worldwide. It studies every phase in the…

Mars Science Laboratory: Curiosity Rover
Part of NASA’s Mars Science Laboratory mission, at the time of launch, Curiosity was the largest and most capable rover…

Science Missions

https://science.nasa.gov/missions/webb/nasas-webb-curiosity-named-in-times-best-inventions-hall-of-fame/
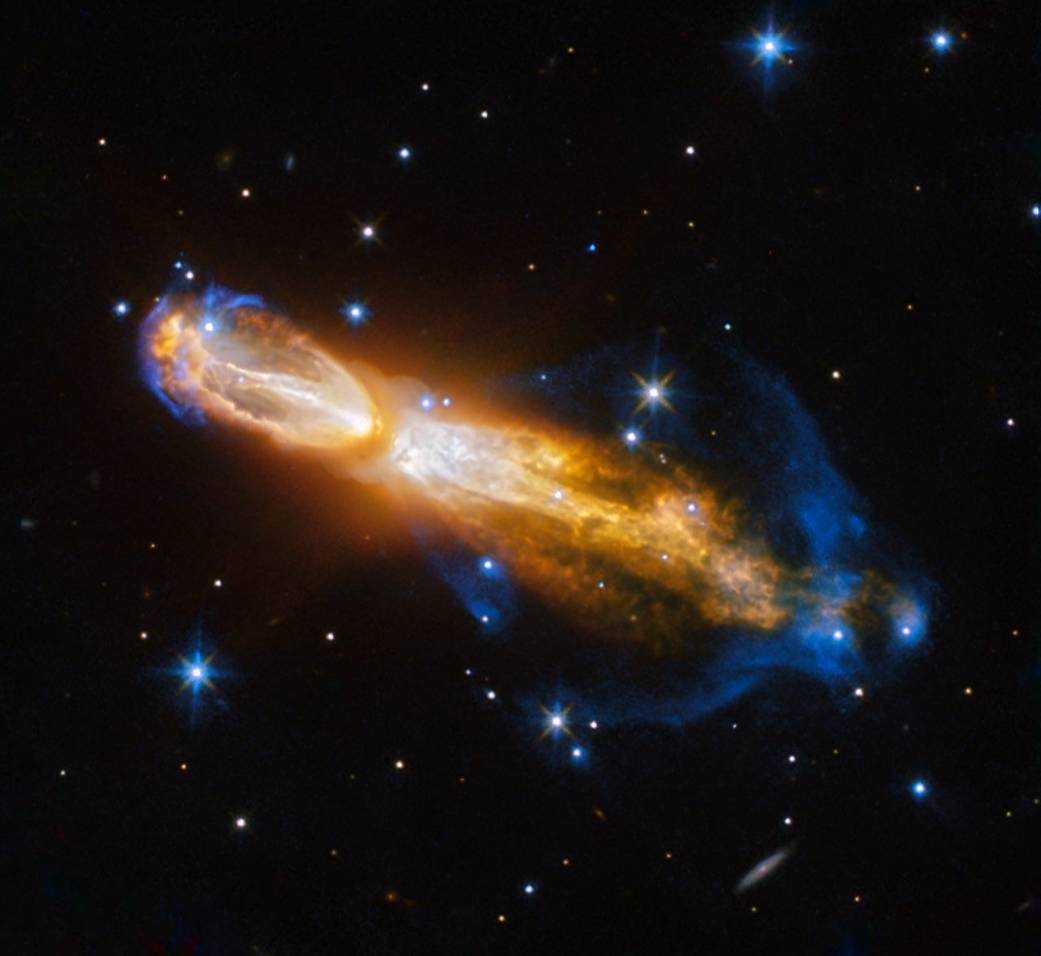
A Rare Gourd
NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope captured an uncommon sight – the death of a low-mass star – in this image of the Calabash Nebula released on Feb. 3, 2017. Here, we can see the star going through a rapid transformation from a red giant to a planetary nebula, during which it blows its outer layers of […]https://www.nasa.gov/image-article/a-rare-gourd/
A Rare Gourd
NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope captured an uncommon sight – the death of a low-mass star – in this image of the Calabash Nebula released on Feb. 3, 2017.
Here, we can see the star going through a rapid transformation from a red giant to a planetary nebula, during which it blows its outer layers of gas and dust out into the surrounding space. The recently ejected material is spat out in opposite directions with immense speed — the gas shown in yellow is moving close to a million kilometers an hour.
Astronomers rarely capture a star in this phase of its evolution because it occurs within the blink of an eye – in astronomical terms. Over the next thousand years the nebula is expected to evolve into a fully-fledged planetary nebula.
https://www.nasa.gov/image-article/a-rare-gourd/
NASA Announces Plan to Map Milky Way With Roman Space Telescope
NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope team has released detailed plans for a major survey that will reveal our home galaxy, the Milky Way, in unprecedented detail. In one month of observations spread across two years, the survey will unveil tens of billions of stars and explore previously uncharted structures. “The Galactic Plane Survey will […]https://www.nasa.gov/missions/roman-space-telescope/nasa-announces-plan-to-map-milky-way-with-roman-space-telescope/
NASA Announces Plan to Map Milky Way With Roman Space Telescope
NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope team has released detailed plans for a major survey that will reveal our home galaxy, the Milky Way, in unprecedented detail. In one month of observations spread across two years, the survey will unveil tens of billions of stars and explore previously uncharted structures.
Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
“The Galactic Plane Survey will revolutionize our understanding of the Milky Way,” said Julie McEnery, Roman’s senior project scientist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. “We’ll be able to explore the mysterious far side of our galaxy and its star-studded heart. Because of the survey’s breadth and depth, it will be a scientific mother lode.”
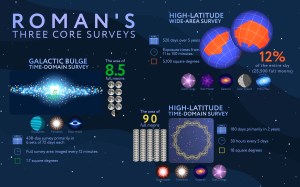
The Galactic Plane Survey is Roman’s first selected general astrophysics survey — one of many observation programs Roman will do in addition to its three core surveys and Coronagraph technology demonstration. At least 25% of Roman’s five-year primary mission is reserved for astronomers worldwide to propose more surveys beyond the core programs, fully leveraging Roman’s capabilities to conduct groundbreaking science. Roman is slated to launch by May 2027, but the team is on track for launch as early as fall 2026.
While ESA’s (European Space Agency’s) retired Gaia spacecraft mapped around 2 billion Milky Way stars in visible light, many parts of the galaxy remain hidden by dust. By surveying in infrared light, Roman will use powerful heat vision that can pierce this veil to see what lies beyond.
“It blows my mind that we will be able to see through the densest part of our galaxy and explore it properly for the first time,” said Rachel Street, a senior scientist at Las Cumbres Observatory in Santa Barbara, California, and a co-chair of the committee that selected the Galactic Plane Survey design.

The survey will cover nearly 700 square degrees (a region of sky as large as about 3,500 full moons) along the glowing band of the Milky Way — our edge-on view of the disk-shaped structure containing most of our galaxy’s stars, gas, and dust. Scientists expect the survey to map up to 20 billion stars and detect tiny shifts in their positions with repeated high-resolution observations. And it will only take 29 days spread over the course of the mission’s first two years.
Cosmic Cradles
Stars are born from parent clouds of gas and dust. Roman will peer through the haze of these nesting grounds to see millions of stellar embryos, newborn stars still swaddled in shrouds of dust, tantrumming toddler stars that flare unpredictably, and young stars that may have planetary systems forming around them. Astronomers will study stellar birth rates across a wide range of masses and stitch together videos that show how stars change over time.
“This survey will study such a huge number of stars in so many different stellar environments that we’ll be sampling every phase of a star’s evolution,” Street said.
Observing so many stars in various stages of early development will shed light on the forces that shape them. Star formation is like a four way tug-of-war between gravity, radiation, magnetism, and turbulence. Roman will help us study how these forces influence whether gas clouds collapse into full-fledged stars, smaller brown dwarfs — in-between objects that are much heavier than planets but not massive enough to ignite like stars — or new worlds.
Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Some stars are born in enormous litters called clusters. Roman will study nearly 2,000 young, loosely bound open clusters to see how the galaxy’s spiral arms trigger star formation. The survey will also map dozens of ancient, densely packed globular clusters near the center of the galaxy that could help astronomers reconstruct the Milky Way’s early history.
Comparing Roman’s snapshots of clusters scattered throughout the galaxy will enable scientists to study nature versus nurture on a cosmic scale. Because a cluster’s stars generally share the same age, origin, and chemical makeup, analyzing them allows astronomers to isolate environmental effects very precisely.
Pulse Check
When they run out of fuel, Sun-like stars leave behind cores called white dwarfs and heavier stars collapse to form neutron stars and black holes. Roman will find these stellar embers even when they’re alone thanks to wrinkles in space-time.
Anything that has mass warps the underlying fabric of the universe. When light from a background star passes through the gravitational well around an intervening object on its journey toward Earth, its path slightly curves around the object. This phenomenon, called microlensing, can temporarily brighten the star. By studying these signals, astronomers can learn the mass and size of otherwise invisible foreground objects.
A separate survey — Roman’s Galactic Bulge Time-Domain Survey — will conduct deep microlensing observations over a smaller area in the heart of the Milky Way. The Galactic Plane Survey will conduct repeated observations over a shorter interval but across the whole center of the galaxy, giving us the first complete view of this complex galactic environment. An unobscured view of the galaxy’s central bar will help astronomers answer the question of its origin, and Roman’s videos of stars in this region will enable us to study some ultratight binary objects at the very ends of their lives thanks to their interactions with close companions.
“Compact binaries are particularly interesting because they’re precursors to gravitational-wave sources,” said Robert Benjamin, a visiting professor at the University of Wisconsin-Whitewater, and a co-chair of the committee that selected the Galactic Plane Survey design. When neutron stars and black holes merge, the collision is so powerful that it sends ripples through the fabric of space-time. “Scientists want to know more about the pathways that lead to those mergers.”
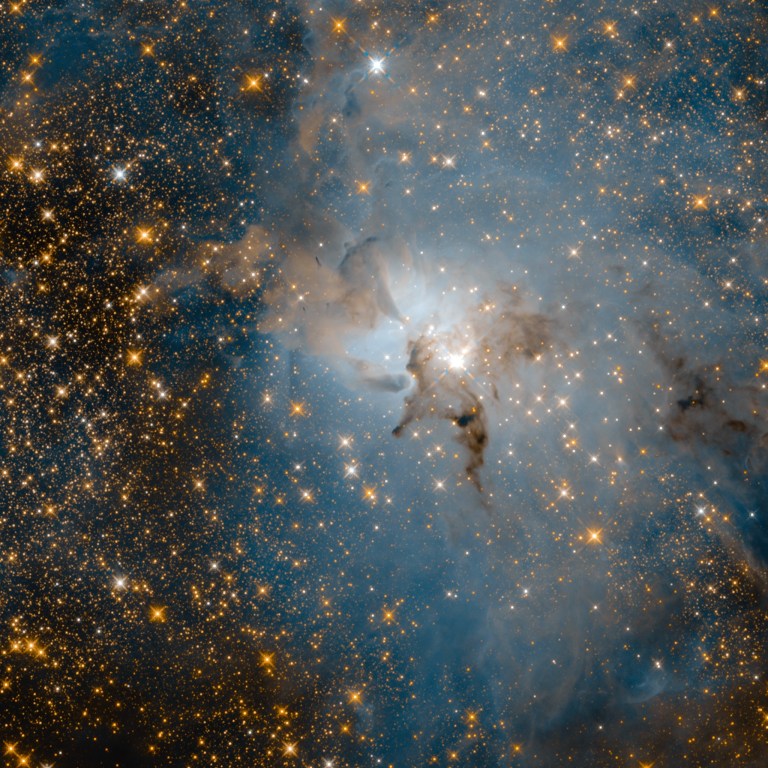






Optical vs infrared
Two Views
Roman’s repeated observations will also monitor stars that flicker. Ground-based surveys detect thousands of bright stellar outbursts, but often can’t see the faint, dust-obscured stars that produce them. Roman will pinpoint the culprits plus take high-resolution snapshots of the aftermath.
Some stars throb rhythmically, and the speed of their pulsing is directly linked to their intrinsic brightness. By comparing their true brightness to how bright they appear from Earth, astronomers can measure distances across the galaxy. Roman will find these blinking stars farther away than ever before and track them over time, helping astronomers improve their cosmic measuring sticks.
“Pairing Roman’s Galactic Plane Survey with other Milky Way observations will create the best portrait of the galaxy we’ve ever had,” Benjamin said.
Download additional images and video from NASA’s Scientific Visualization Studio.
For more information about the Roman Space Telescope, visit:
By Ashley Balzer
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.
Media contact:
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.
301-286-1940
Explore More
Details
https://www.nasa.gov/missions/roman-space-telescope/nasa-announces-plan-to-map-milky-way-with-roman-space-telescope/